Cybele, the great mother, powerful goddess of nature, is recognizable in this little statue seated on a throne between two lions and found in the waters of the port of Puteoli, even though the artefact is heavily eroded and damaged by marine organisms.
The iconographic scheme is very traditional and often recurs in the whole Roman world, originating probably from the model of the cult statue of Metroon of Athens, sculpted by Agorakritos around 420 B.C.
The iconographic scheme of Cybele between the lions in a replica from Nicaea in Bithynia, today at the Archaeological Museum of Istanbul.
The statue, heavily deprived of the most part of the outer stone layer, presents a widespread and significant biological alteration caused by boring sponges from the family Clionaidae. This degradation exposed various layers of marble, as it can be clearly observed in the figure below.
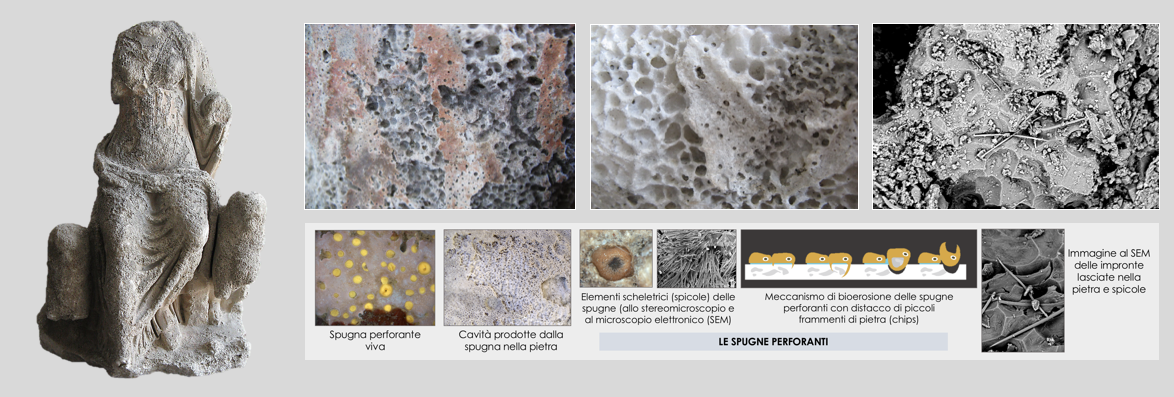
Davidde B., Ricci S., Poggi D., Bartolini M., 2010. Marine bioerosion of stone artefacts preserved in the Museo Archeologico dei Campi Flegrei in the Castle of Baia (Naples), Archaeologia Maritima Mediterranea; 7: 75-115.
Demma, F. (2010) ‘Scultori, redemptores, marmorarii ed officinae nella Puteoli romana. Fonti storiche ed archeologiche per lo studio del problema’, Mélanges de l’Ecole française de Rome. Antiquité, 122(2), pp. 399–425.
Ricci S., Sacco Perasso C., Antonelli, F., Davidde Petriaggi B., 2015. Marine Bivalves colonizing roman artefacts recovered in the Gulf of Pozzuoli and in the Blue Grotto in Capri (Naples, Italy): boring and nestling species. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation (98) 89 – 100.
Ricci, S., Pietrini, A. M., Bartolini, M., Sacco Perasso, C., 2013. Role of the microboring marine organisms in the deterioration of archaeological submerged lapideous artifacts (Baia, Naples, Italy). International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 82 (2013) 199-206.
Ricci S., Davidde B., Bartolini M., Priori G. F., 2009. Bioerosion of lapideous objects found in the underwater archaeological site of Baia (Naples). Archaeologia Maritima Mediterranea, 6: 167-188.
Zevi F. (cur.) 2009, Museo archeologico dei Campi Flegrei. Castello di Baia. Napoli: Electa Napoli, vol. 2, p. 56.



